ADVANCED LAPAROSCOPIC GI & GI CANCER SURGERY
- /
- Advanced Laparoscopic Gi & GI Cancer Surgery
ADVANCED LAPAROSCOPIC GI & GI CANCER SURGERY
Oesophagectomy (Cancer of Oesophagus)
Oesophagus is also called as food pipe. The surgery to remove a part of Oesophagus or complete removal is called Oesophagectomy. We are doing Oesophagectomy by minimally invasive technique. Laparoscopically removal of oesophagus or part of it and using stomach or part of large intestine to reconstruct it depending upon the stage of tumour Oesophagectomy is decided.

There are 3 types of Oesophagectomy techniques.
- Open - Use one or more large cuts in neck, chest or abdomen.
- Done through laparoscopy- where few small cuts in abdomen and surgery is done.
- Laparoscopic Technique has lots of advantages over open techniques terms of comfort, recovery and duration of Hospital staff.
Laparoscopic Surgery for Hiatus Hernia (FUNDOPLICATION)
Laparoscopic Hiatus Hernia repair with Nissan’s fundoplications (for Hiatus Hernia and reflux). Hiatus hernia is a disease in which there is chronic heartburn because of acid reflux from the stomach to the esophagus due to an incompetent lower oesophagus sphincter. In Hiatus Hernia when the stomach or its part slides into the chest this causes and refluxes. We are doing this procedure very commonly.
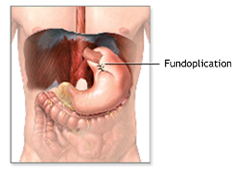
This procedure is done laparoscopically in which Gastroesophageal junction is dissected hiatus is repaired with sutures or Mesh Depending upon the size of the detecting in crura and a wrap from the top of the stomach to the lower end of the stomach to treat an artificial value which prevents the refuse.
Advantages:
- One hr procedure.
- Excellent results.
- Return to work in 4-5days
Indication:
- Long term medical treatment with not desired effect.
- GERD with its complications i.e. Barrette Oesophagus, peptide structure.
- Patient Wish to stop medical treatment.
- Mixed Para Oesophageal Hernia.
- Recurrent reflux or Complication after previous anti reflux surgery.
Laparoscopic Achalasia Cardia Surgery (Heller’s Cardiomyotomy)
- This can be in any age group.
- It affects both age groups.
- Pain problem is in swelling solids and liquid food, chest pain and regurgitation.
- Dysphasia and weight loss
Stomach Cancer
Partial Gastrectomy
A partial gastrectomy is the surgical removal of a portion of the stomach, as opposed to a total gastrectomy in which the entire stomach is removed. A gastrectomy may also be accompanied by a vagotomy (removal of the part of the vagus nerve that stimulates the stomach’s acid production for digestion).
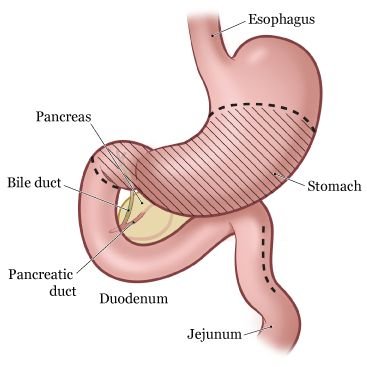
Total Gastrectomy
A total gastrectomy involves removing your whole stomach, nearby lymph nodes, and parts of your esophagus and small intestine. Your esophagus is reconnected to your small intestine so you can continue to eat and swallow
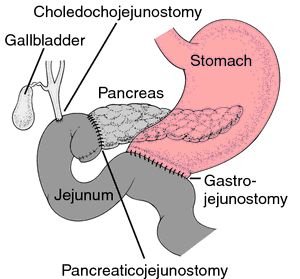
Whipple Procedure (For Pancreatic Cancer)
Pancreatic cancer is the common cancer which is having poor prognosis. Till the time it shows the symptoms it spreads longer before. Whipple’s procedure is a complex surgery which extends the life of patient and has the possibility of curing Pancreatic/ Periampullary Cancer as well.The life Expectancy op patient of Pancreatic Cancer depends upon the site and stage of tumour. The Pt. survival definitely increases by Whipple’s procedure.
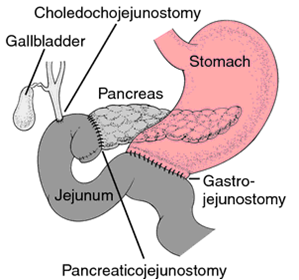
Whipple’s procedure is routinely performed in an centre. In this procedure Head of Pancreases duodenum (Portion of Common Bile Duct, Gall Bladder and sometimes part of stomach) is removed and reconstruction is done. Very few patients are eligible by laparoscopic Whipple’s procedure.
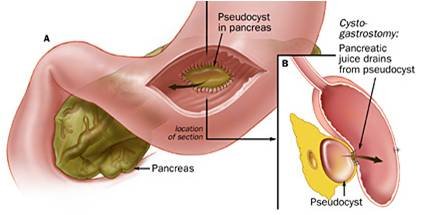
Laparoscopy For Pancreatic Pseudocyst
Pancreas is very important organ located behind the stomach. It is spongy tad pole shaped organ having function of making enzymes which helps in digestion of the food and hormone to regulate the blood sugar level.
Laparoscopic Splenectomy
Laparoscopic splenectomy is a key hole surgery to remove all or a part of your spleen. The spleen is a bean-shaped organ found under the ribs on the left upper side of stomach. The function of spleen is to remove old and damaged blood cells as blood passes through it and also makes immune system cells, known as lymphocytes, which help to fight germs and infections.
Radical Cholecystectomy (For Cancer Gall Bladder)
Extended (Radical) Cholecystectomy is often, an extended cholecystectomy is used for patients with gallbladder cancer to decrease the risk of recurrence. This involves removing the gallbladder, part of the liver, and several lymph nodes.
Choledochoduodenostomy
Choledochoduodenostomy (CDD) is a surgical procedure to create an anastomosis, a surgical connection, between the common bile duct (CBD) and an alternative portion of the duodenum.
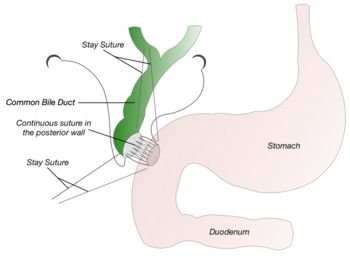
Choledochojejunostomy
Choledochojejunostomy is a procedure for creating an anastomosis of the common bile duct (CBD) to the jejunum, performed to relieve symptoms of biliary obstruction and restore continuity to the biliary tract.
For
1. Bile Duct Stone : Bile duct stones are gallstones in the bile duct. They can start in the gallbladder and migrate into the bile duct or they can form in the bile duct itself. The stones can become lodged in the bile duct, causing a blockage.
2. Bile Duct Stricture: A bile duct stricture is an abnormal narrowing of the common bile duct. This is a tube that moves bile from the liver to the small intestine. Bile is a substance that helps with digestion.
Hepaticojejunostomy
A hepaticojejunostomy is the surgical creation of a communication between the hepatic duct and the jejunum; a choledochojejunostomy is the surgical creation of a communication between the common bile duct (CBD) and the jejunum. Oskar Sprengel published the first report of a choledochoenterostomy in 1891
Hepaticojejunostomy For
- CBD for Cancer
- Bile Duct Injury
Liver Cancer
Laparoscopic Liver Cyst Excision
Simple Cysts
Simple cysts are fluid-filled sacs, or cysts, that can form in one or both of your kidneys. You can have just one cyst or you can have many. Simple kidney cysts are usually round or oval in shape. They can range from the size of a pea to the size of a golf ball.
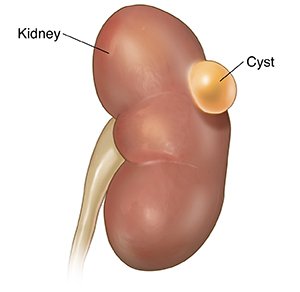
Hydatid Cysts
The larval form of the tapeworm may lodge in various body sites where they form a fluid-filled sac known as a hydatid cyst. The cysts contain immature forms of the tapeworm and can increase in size from 5–10 cm or more over a period of time. While some cysts may die, others can remain alive for many years.

Laparoscopic Colorectal Surgery
Laparoscopic Right Hemicolectomy
Laparoscopic Left Hemicolectomy
This may be performed for cancers of the tumours of the colon or for diverticulitis. A segment of the colon is removed and the ends reconnected.
Laparoscopic Sigmoid Colectomy
The sigmoid colon is most frequently involved in diverticulitis. Removal of this portion of the colon involves reconnection of the colon to the rectum. The sigmoid may also be removed for cancer or tumours.
Abdominal Perineal Resection (APR)
APR is a surgery that’s done to treat anal or rectal cancer. To remove the cancer, your surgeon will remove all of the following: The lower part of your colon. Your rectum.
Laparoscopic Low Anterior Resection for Cancer Rectum
There are situations when diversion of the faecal stream is required. During this procedure, a portion of the intestine is brought out to the skin level so that the stool can be diverted away from bowel downstream.
Laparoscopic Total Proctocolectomy
For some patients with Ulcerative colitis, the entire colon and rectum may be removed laparoscopically. Following removal, creation of a pouch using the small intestine may allow one to avoid a permanent end ileostomy.
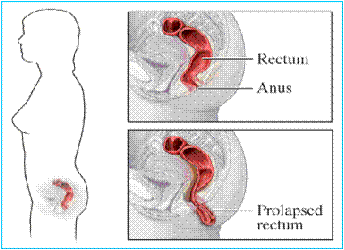
Laparoscopic For Rectal Prolapse
What is rectal prolapse?
In rectal prolapsed, the lower end of the colon which located just above the anus is called rectum, becomes stretched out and protrudes out of the anus. This condition of rectum is the weakness of the anal sphincter muscle and most of times associated with rectal prolapse, leading to holding stool, leakage of stool or mucus.
Laparoscopic lleocecectomy Surgery
Laparoscopic Rectopexy
Rectal prolapse is a condition where the rectum bulges out of the anal opening. Repair of rectal prolapse can be accomplished laparoscopically in many cases. The goal of ECU surgeons is to provide safe and effective treatment for each patient. At times, it may be advantageous or safest to have a somewhat larger incision to have a particular procedure. In this case, each of the above operations may be accomplished with open techniques.
Colostomy or Iiioestomy
There are situations when diversion of the fecal stream is required. During this procedure, a portion of the intestine is brought out to the skin level so that the stool can be diverted away from bowel downstream.
Other Procedures:
i) Combined Laparoscopic/ Endoscopic Resections
For benign tumours, which may not able to be removed with colonoscopy alone, at times surgeons may combine colonoscopy with Laparoscopic techniques to remove an advanced polyp or benign tumour.
ii) Trans- Anal Excision
For benign tumours of the middle and lower rectum, excision using instruments through the anus may be offered. This avoids all scars on the skin and allows for a very fast recovery following surgery.

